Adaptive Vision Transformer for Event-Based Human Pose Estimation (ACM MM 2024)
Abstract
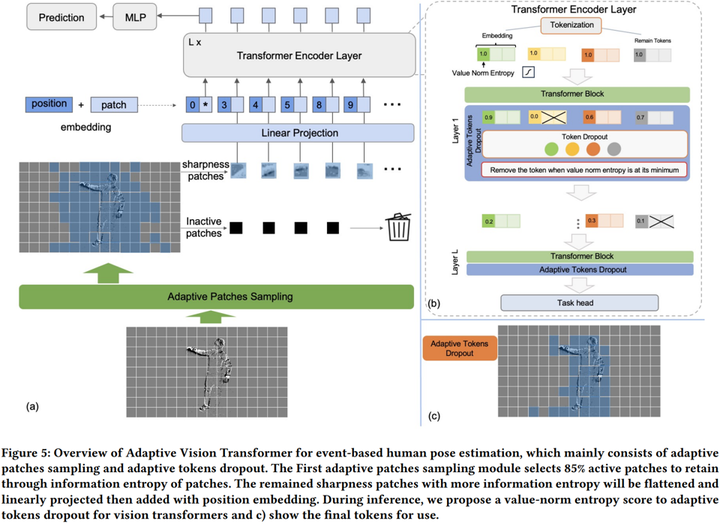
Event-based human pose estimation has gained popularity due to the benefits of high temporal resolution and high dynamic range offered by event cameras. The inherent spatial sparsity of event data makes discarding less significant regions a straightforward and effective way to decrease the computation. However, implementing this operation in CNNs poses a challenge, as it disrupts the regularity of dense convolutional workload. In this paper, we propose an adaptive vision transformer, a novel efficient backbone for human pose estimation with event cameras. Specifically, we present two adaptive patch and token sampling approaches based on the characteristics of events, thereby reducing the computational load while still achieving comparable performance. Firstly, we design an adaptive patch sampling scheme to eliminate inactivity patches by assessing the entropy of the events before they are inputted into the transformer. Secondly, we further propose an adaptive token reduction strategy to selectively remove less informative tokens in transformer layers through a dynamic token pruning algorithm. To exploit event-based visual cues in human pose estimation tasks, we construct a large-scale frame-event-based dataset, dubbed Event Multi Movement HPE (EventMM HPE). The dataset provides annotation frequencies up to 240 Hz. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in estimation accuracy.